As we mentioned before access control system is a set of elements that to a large extent combines supervisory software with executive devices to perform specific activities and their registration in a database.
Unlike systems based on passive RFID, systems Active RFID operate with a larger reading range thanks to the built-in battery transponder increasing transmission power. Increased coverage in this case is paid for by shorter operating time and a larger transponder size, but in some applications this approach is crucial.
The hardware components of an active access control system include ACTS-2 long range readers, which are connected to the control system via RS232 / RS485, WIEGAND or 1-Wire interfaces, which, based on read user rights from transponders ATPLA-S/N by controlling an electric lock, electric lock or other device such as: turnstile, gate, barrier - will allow the user to enter / enter a given zone. A special feature of ATPLA-S transponders is the ability to read them from a distance of up to 5 meters when they are in the field of operation of the ACTS-2 reader (125kHz), while ATPLA-N (869MHz) transponders thanks to cyclic ID transmission can reach a range of up to 200 meters. ATPLA-N and ATPLA-S transponders have their own unique ID up to 4 bytes long and can be programmed by system administrators using a reader and programmer PAC-AU connected to any computer via a USB interface.
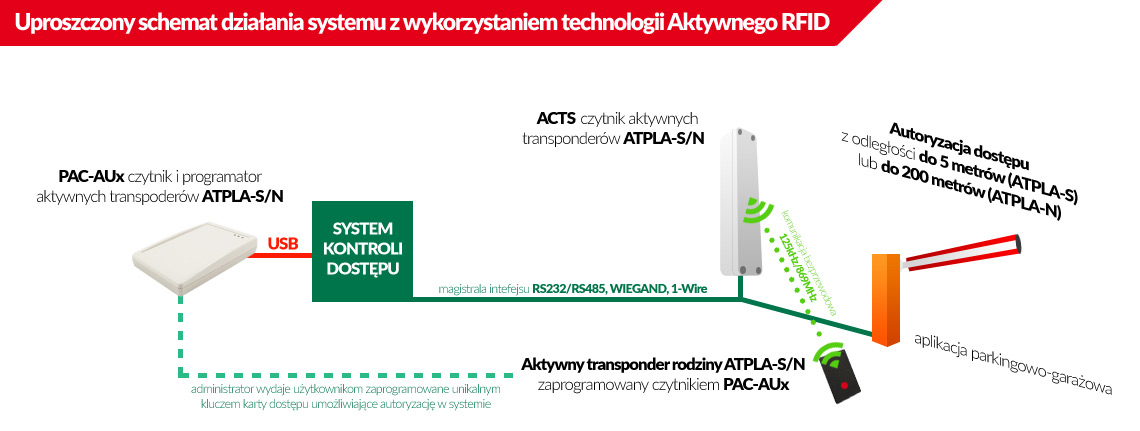
An example of such an application can be, for example, a system in which the ATPLA-S transponder is located in the vehicle (perhaps permanently) and maintenance-free controls, for example, a garage door or a parking barrier. As with any RFID application, the applications are almost limitless and depend only on the creativity of the designer.






